Downloads
Download
Additional Files
Download - Supplementary Materials


This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Article
Vascular and Metabolic Responses to Elevated Circulating PDGF-BB in Mice: A Multiparametric MRI Study
Xiuli Yang 1,†, Jiekang Wang 2,3,†, Yuguo Li 1,4, Mei Wan 2,3,*, Zhiliang Wei 1,4,*
1 Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
3 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
4 F. M. Kirby Research Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Research Institute, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
* Correspondence: mwan4@jhmi.edu (M.W.); zhiliang.wei@jhu.edu (Z.W.)
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
Received: 20 November 2024; Revised: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 22 January 2025; Published: 11 February 2025
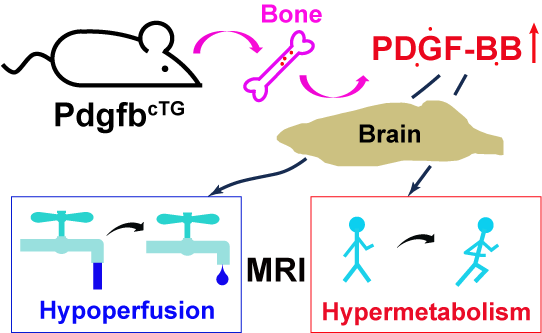
Abstract: Elevated circulating platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) has been implicated in the development of various aged-related pathologies and is recognized as a potential pro-aging factor. Although numerous studies have explored the pathological roles of the PDGF-BB/PDGFRβ signaling pathway, few investigations have dissected its function in neurofunctional responses to elevated circulating PDGF-BB, primarily because in-vivo measurements are generally required to assess neurofunction. To address this knowledge gap, we characterized the vascular and metabolic responses to elevated circulating PDGF-BB in vivo using multiparametric non-invasive non-contrast MRI techniques in a conditional Pdgfb transgenic mouse model (PdgfbcTG) at 6 months of age. Results indicated that PdgfbcTG mice exhibited decreased cerebral blood flow (p = 0.025), elevated oxygen extraction (p = 0.002), and increased metabolic rate of oxygen (p = 0.035), mirroring the changes observed in human aging. The rate of change in vascular and metabolic measurements in the model mice was significantly higher (≥200.3%) compared to that of naturally aged mice. This study provides neurofunctional evidence that elevated circulating PDGF-BB accelerates neurovascular aging.
Keywords:
PDGF-BB cerebral blood flow oxygen extraction fraction cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen relaxation time diffusionReferences
- Santhanam, L.; Liu, G.; Jandu, S.; Su, W.; Wodu, B.P.; Savage, W.; Poe, A.; Liu, X.; Alexander, L.M.; Cao, X.; et al. Skeleton-secreted PDGF-BB mediates arterial stiffening. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e147116. doi: 10.1172/JCI147116
- Wang, J.; Fang, C.L.; Noller, K.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G.; Shen, K.; Song, K.; Cao, X.; Wan, M. Bone-derived PDGF-BB drives brain vascular calcification in male mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e168447. doi: 10.1172/JCI168447
- Mitlak, B.H.; Finkelman, R.D.; Hill, E.L.; Li, J.; Martin, B.; Smith, T.; D’Andrea, M.; Antoniades, H.N.; Lynch, S.E. The effect of systemically administered PDGF-BB on the rodent skeleton. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 238–247. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650110213
- Lindahl, P.; Johansson, B.R.; Levéen, P.; Betsholtz, C. Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science 1997, 277, 242–245. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5323.242
- Hellström, M.; Kalén, M.; Lindahl, P.; Abramsson, A.; Betsholtz, C. Role of PDGF-B and PDGFR-beta in recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes during embryonic blood vessel formation in the mouse. Development 1999, 126, 3047–3055. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.14.3047
- Cicognola, C.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; van Westen, D.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Palmqvist, S.; Ahmadi, K.; Strandberg, O.; Stomrud, E.; Janelidze, S.; et al. Associations of CSF PDGFRβ with aging, blood-brain barrier damage, neuroinflammation, and Alzheimer disease pathologic changes. Neurology 2023, 101, e30–e39. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207358
- Butts, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, W.T.; Kehoe, P.G.; Miners, J.S.; Verble, D.D.; Zetterberg, H.; Zhao, L.; Trotti, L.M.; Benameur, K.; et al. sPDGFRβ and neuroinflammation are associated with AD biomarkers and differ by race: The ASCEND study. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 1175–1189. doi: 10.1002/alz.13457
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Fang, C.L.; Shen, K.; Qian, C.; Qi, C.; Li, T.; Gao, P.; Wong, P.C.; et al. Elevated PDGF-BB from bone impairs hippocampal vasculature by inducing PDGFRβ shedding from pericytes. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206938. doi: 10.1002/advs.202206938
- Kapoor, A.; Nation, D.A. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB and white matter hyperintensity burden in APOE4 carriers. Cereb. Circ. Cogn. Behav. 2022, 3, 100131. doi: 10.1016/j.cccb.2022.100131
- Smyth, L.C.D.; Highet, B.; Jansson, D.; Wu, J.; Rustenhoven, J.; Aalderink, M.; Tan, A.; Li, S.; Johnson, R.; Coppieters, N.; et al. Characterisation of PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling pathways in human brain pericytes: Evidence of disruption in Alzheimer’s disease. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 235. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03180-8
- Gianni, D.; Zambrano, N.; Bimonte, M.; Minopoli, G.; Mercken, L.; Talamo, F.; Scaloni, A.; Russo, T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces the beta-gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein through a Src-Rac-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9290–9297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211899200
- Liu, G.; Shu, W.; Chen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Fang, S.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, W.; Lin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; et al. Bone-derived PDGF-BB enhances hippocampal non-specific transcytosis through microglia-endothelial crosstalk in HFD-induced metabolic syndrome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 111. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03097-5
- Fang, C.L.; Liu, B.; Wan, M. “Bone-SASP” in skeletal aging. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2023, 113, 68–82. doi: 10.1007/s00223-023-01100-4
- Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Hirschler, L.; Barbier, E.L.; Li, T.; Wong, P.C.; Lu, H. Brain metabolism in tau and amyloid mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease: An MRI study. NMR Biomed. 2021, 34, e4568. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4568
- Wei, Z.; Chen, L.; Hou, X.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Xu, J.; Lu, H. Age-related alterations in brain perfusion, venous oxygenation, and oxygen metabolic rate of mice: A 17-month longitudinal MRI study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 559. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00559
- Wei, Z.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, D.; Xu, J.; Liu, P.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Lu, H. Optimization of phase-contrast MRI for the estimation of global cerebral blood flow of mice at 11.7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2566–2575. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27592
- Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Lu, H. Quantitative assessment of cerebral venous blood T2 in mouse at 11.7T: Implementation, optimization, and age effect. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 521–528. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27046
- Hirschler, L.; Debacker, C.S.; Voiron, J.; Kohler, S.; Warnking, J.M.; Barbier, E.L. Interpulse phase corrections for unbalanced pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling at high magnetic field. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 1314–1324. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26767
- Kety, S.S.; Schmidt, C.F. The nitrous oxide method for the quantitative determination of cerebral blood flow in man: Theory, procedure and normal values. J. Clin. Investig. 1948, 27, 476–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI101994
- Pires Monteiro, S.; Hirschler, L.; Barbier, E.L.; Figueiredo, P.; Shemesh, N. High-resolution perfusion imaging in rodents using pCASL at 9.4 T. bioRxiv 2024, bioRxiv:03.07.583839. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.07.583839
- Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Han, Z.; Xu, J.; McMahon, M.T.; Duan, W.; Liu, G.; Lu, H. Quantitative cerebrovascular reactivity MRI in mice using acetazolamide challenge. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 88, 2233–2241. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29353
- Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, Z.; Yao, M.; Li, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Duan, W.; Lu, H. Non-contrast assessment of blood-brain barrier permeability to water in mice: An arterial spin labeling study at cerebral veins. Neuroimage 2023, 268, 119870. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.119870
- Lu, H.; Ge, Y. Quantitative evaluation of oxygenation in venous vessels using T2-Relaxation-Under-Spin-Tagging MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 357–363. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21627
- Yang, X. Improving the reliability of T2 measurement in magnetic resonance imaging. bioRxiv 2024, bioRxiv:06.09.598128. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.09.598128
- Wei, Z.; Roh, S.E.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Bibic, A.; Lu, H. The impact of isoflurane anesthesia on brain metabolism in mice: An MRI and electroencephalography (EEG) study. NMR Biomed. 2024, 37, e5260. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5260
- Leithner, C.; Muller, S.; Fuchtemeier, M.; Lindauer, U.; Dirnagl, U.; Royl, G. Determination of the brain-blood partition coefficient for water in mice using MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1821–1824. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.160
- Meyer, C.E.; Kurth, F.; Lepore, S.; Gao, J.L.; Johnsonbaugh, H.; Oberoi, M.R.; Sawiak, S.J.; MacKenzie-Graham, A. In vivo magnetic resonance images reveal neuroanatomical sex differences through the application of voxel-based morphometry in C57BL/6 mice. Neuroimage 2017, 163, 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.027
- Li, W.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Quantitative theory for the transverse relaxation time of blood water. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4207. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4207
- Ulatowski, J.A.; Oja, J.M.E.; Suarez, J.I.; Kauppinen, R.A.; Traystman, R.J.; van Zijl, P.C.M. In vivo determination of absolute cerebral blood volume using hemoglobin as a natural contrast agent: An MRI study using altered arterial carbon dioxide tension. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999, 19, 809–817. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199907000-00012
- Lin, A.L.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, X.; Duong, T.Q. Blood longitudinal (T1) and transverse (T2) relaxation time constants at 11.7 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Mater.Phys. Biol. Med. 2012, 25, 245–249. doi: 10.1007/s10334-011-0287-2
- Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Bibic, A.; Duan, W.; Xu, J.; Lu, H. Toward accurate cerebral blood flow estimation in mice after accounting for anesthesia. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1169622. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1169622
- Lu, H.; Xu, F.; Grgac, K.; Liu, P.; Qin, Q.; van Zijl, P. Calibration and validation of TRUST MRI for the estimation of cerebral blood oxygenation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 67, 42–49. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22970
- Hall, C.N.; Reynell, C.; Gesslein, B.; Hamilton, N.B.; Mishra, A.; Sutherland, B.A.; O’Farrell, F.M.; Buchan, A.M.; Lauritzen, M.; Attwell, D. Capillary pericytes regulate cerebral blood flow in health and disease. Nature 2014, 508, 55–60. doi: 10.1038/nature13165
- Faraci, F.M.; Breese, K.R.; Heistad, D.D. Cerebral vasodilation during hypercapnia. Role of glibenclamide-sensitive potassium channels and nitric oxide. Stroke 1994, 25, 1679–1683. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.25.8.1679
- Peterson, E.C.; Wang, Z.; Britz, G. Regulation of cerebral blood flow. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2011, 2011, 823525. doi: 10.1155/2011/823525
- Segarra, M.; Aburto, M.R.; Acker-Palmer, A. Blood-brain barrier dynamics to maintain brain homeostasis. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 393–405. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.12.002
- Xiong, B.; Li, A.; Lou, Y.; Chen, S.; Long, B.; Peng, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; et al. Precise cerebral vascular atlas in stereotaxic coordinates of whole mouse brain. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 128. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00128
- Winkler, E.A.; Bell, R.D.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericyte-specific expression of PDGF beta receptor in mouse models with normal and deficient PDGF beta receptor signaling. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 32. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-32
- Perosa, V.; Priester, A.; Ziegler, G.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Dobisch, L.; Spallazzi, M.; Assmann, A.; Maass, A.; Speck, O.; Oltmer, J.; et al. Hippocampal vascular reserve associated with cognitive performance and hippocampal volume. Brain 2020, 143, 622–634. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz383
- Heldin, C.H.; Westermark, B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1283–1316. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.4.1283
- Smeitink, J.; van den Heuvel, L.; DiMauro, S. The genetics and pathology of oxidative phosphorylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 342–352. doi: 10.1038/35072063
- Lu, H.; Xu, F.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Cheng, Y.; Flicker, B.; Hebrank, A.C.; Uh, J.; Park, D.C. Alterations in cerebral metabolic rate and blood supply across the adult lifespan. Cereb. Cortex. 2011, 21, 1426–1634. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq224
- Deery, H.A.; Liang, E.; Di Paolo, R.; Voigt, K.; Murray, G.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Egan, G.F.; Moran, C.; Jamadar, S.D. The association of regional cerebral blood flow and glucose metabolism in normative ageing and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65396-4
- Nagata, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Takano, D.; Maeda, T.; Fujimaki, Y.; Nakase, T.; Sato, Y. Cerebral circulation in aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 30, 49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.06.001
- Peng, S.L.; Dumas, J.A.; Park, D.C.; Liu, P.; Filbey, F.M.; McAdams, C.J.; Pinkham, A.E.; Adinoff, B.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Age-related increase of resting metabolic rate in the human brain. Neuroimage 2014, 98, 176–183. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.078
- Amorim, J.A.; Coppotelli, G.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M.; Ross, J.M.; Sinclair, D.A. Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 243–258. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00626-7
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.200
- Sikka, G.; Miller, K.L.; Steppan, J.; Pandey, D.; Jung, S.M.; Fraser, C.D., 3rd; Ellis, C.; Ross, D.; Vandegaer, K.; Bedja, D.; et al. Interleukin 10 knockout frail mice develop cardiac and vascular dysfunction with increased age. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2012.11.001
- Braun, D.J.; Abner, E.; Bakshi, V.; Goulding, D.S.; Grau, E.M.; Lin, A.L.; Norris, C.M.; Sudduth, T.L.; Webster, S.J.; Wilcock, D.M.; et al. Blood flow deficits and cerebrovascular changes in a dietary model of hyperhomocysteinemia. ASN Neuro 2019, 11, 1–13. doi: 10.1177/1759091419865788
- Joutel, A.; Monet-Lepretre, M.; Gosele, C.; Baron-Menguy, C.; Hammes, A.; Schmidt, S.; Lemaire-Carrette, B.; Domenga, V.; Schedl, A.; Lacombe, P.; et al. Cerebrovascular dysfunction and microcirculation rarefaction precede white matter lesions in a mouse genetic model of cerebral ischemic small vessel disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 433–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI39733
- Ma, H.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Parsons, M.W.; Churilov, L.; Levi, C.R.; Hsu, C.; Kleinig, T.J.; Wijeratne, T.; Curtze, S.; Dewey, H.M.; et al. Thrombolysis guided by perfusion imaging up to 9 h after onset of stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1795–1803. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1813046
- Shetty, A.N.; Lucke, A.M.; Liu, P.; Sanz Cortes, M.; Hagan, J.L.; Chu, Z.D.; Hunter, J.V.; Lu, H.; Lee, W.; Kaiser, J.R. Cerebral oxygen metabolism during and after therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A feasibility study using magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2019, 49, 224–233. doi: 10.1007/s00247-018-4283-9
- Thomas, B.P.; Sheng, M.; Tseng, B.Y.; Tarumi, T.; Martin-Cook, K.; Womack, K.B.; Cullum, M.C.; Levine, B.D.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Reduced global brain metabolism but maintained vascular function in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 1508–1516. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16658662
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Q.; Modi, H.R.; Cho, S.-M.; Geocadin, R.G.; Thakor, N.V.; Lu, H. Acute-stage MRI cerebral oxygen consumption biomarkers predict 24-h neurological outcome in a rat cardiac arrest model. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4377. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4377
- Guo, Y.; Cho, S.-M.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Q.; Modi, H.R.; Gharibani, P.; Lu, H.; Thakor, N.V.; Geocadin, R.G. Early thalamocortical reperfusion leads to neurologic recovery in a rodent cardiac arrest model. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 37, 60–72. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01432-9
- Lin, Z.; Sur, S.; Soldan, A.; Pettigrew, C.; Miller, M.; Oishi, K.; Bilgel, M.; Moghekar, A.; Pillai, J.J.; Albert, M.; et al. Brain oxygen extraction by using MRI in older individuals: Relationship to apolipoprotein E genotype and amyloid burden. Radiology 2019, 292, 140–148. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182726
- Han, X.; Liu, G.; Lee, S.S.; Yang, X.; Wu, M.N.; Lu, H.; Wei, Z. Metabolic and vascular imaging markers for investigating Alzheimer’s disease complicated by sleep fragmentation in mice. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1456690. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1456690
- Li, S.; Kang, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, W.; Lin, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Cai, S. Sub-second whole brain T(2)mapping via multiband SENSE multiple overlapping-echo detachment imaging and deep learning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 195027. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acfb71
- Hamilton, J.I.; Pahwa, S.; Adedigba, J.; Frankel, S.; O’Connor, G.; Thomas, R.; Walker, J.R.; Killinc, O.; Lo, W.C.; Batesole, J.; et al. Simultaneous mapping of T(1) and T(2) using cardiac magnetic resonance fingerprinting in a cohort of healthy subjects at 1.5T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1044–1052. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27155
- Ren, Y.; Chu, X.; Senarathna, J.; Bhargava, A.; Grayson, W.L.; Pathak, A.P. Multimodality imaging reveals angiogenic evolution in vivo during calvarial bone defect healing. Angiogenesis 2024, 27, 105–119. doi: 10.1007/s10456-023-09899-0
- Chong, S.P.; Merkle, C.W.; Leahy, C.; Srinivasan, V.J. Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) assessed by combined Doppler and spectroscopic OCT. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 3941–3951. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.003941
- Lin, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, K.-K.; Liu, Y.; Shen, G.; Fan, H.; Dong, J. Deciphering the metabolic perturbation in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: A 1 H NMR-based metabolomics study. Parasites Vec. 2019, 12, 300. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3554-0
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Z.; Huang, C.; Lin, D. Taurine alleviates ferroptosis-induced metabolic impairments in C2C12 myoblasts by stabilizing the labile iron pool and improving redox homeostasis. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 3444–3459. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00123
- Peng, S.L.; Su, P.; Wang, F.N.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H.; Liu, P. Optimization of phase-contrast MRI for the quantification of whole-brain cerebral blood flow. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 1126–1133. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24866
- Liu, P.; Xu, F.; Lu, H. Test-retest reproducibility of a rapid method to measure brain oxygen metabolism. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 69, 675–681. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24295
- Jiang, D.; Lu, H.; Parkinson, C.; Su, P.; Wei, Z.; Pan, L.; Tekes, A.; Huisman, T.A.; Golden, C.W.; Liu, P. Vessel-specific quantification of neonatal cerebral venous oxygenation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1129–1139. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27788