Downloads
Download

Kawabata, K., Hoshino, T., & Takeoka, Y. Development of a Temperature-Responsive Polymer Network with Enhanced Transparency and Volume Shrinkage via Star-Shaped PEG-b-PNIPA Block Copolymer. Materials and Interfaces. 2025, 2(2), 285–301. doi: https://doi.org/10.53941/mi.2025.100022
Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
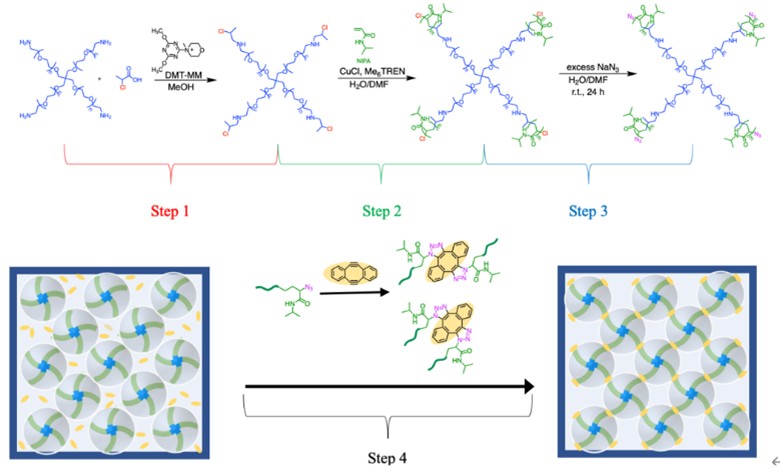
In this study, a temperature-responsive polymer network was successfully synthesized by using a 4-arm star-shaped polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivative as an initiator and polymerizing N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPA) as a secondary acrylamide. The resulting star-shaped block copolymer was used as a building block to prepare a polymer network. Detailed analysis of the polymerization process (including SEC and ¹H NMR) confirmed the successful synthesis and high control over the star-shaped block copolymer structure. The obtained star-shaped block copolymer was crosslinked under semi-dilute conditions via a click reaction, incorporating the hydrophilic PEG into the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPA) network. This network exhibits a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) behavior at 32.5°C in water. The introduction of PEG led to unique properties, such as volume shrinkage upon heating while maintaining optical transparency, due to the effective suppression of phase separation within the network. This advancement overcomes the limitations of conventional PNIPA-based gels and expands their potential applications in optical sensors, actuators, and biomedical devices. The results highlight the promising applications of this polymer network in the development of advanced smart materials.
References
- Seuring, J.; Agarwal, S. Polymers with Upper Critical Solution Temperature in Aqueous Solution: Unexpected Properties from Known Building Blocks. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 597–600. https://doi.org/10.1021/mz400227y.
- Zhang, Q.L.; Hoogenboom, R. Polymers with upper critical solution temperature behavior in alcohol/water solvent mixtures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 48, 122–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2015.02.003.
- Cook, M.T.; Haddow, P.; Kirton, S.B.; McAuley, W.J. Polymers Exhibiting Lower Critical Solution Temperatures as a Route to Thermoreversible Gelators for Healthcare. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008123. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202008123.
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.P.; Lu, M.; Qi, D.M.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Zhong, Q. Synergistic Stain Removal Achieved by Controlling the Fractions of Light and Thermo Responsive Components in the Dual-Responsive Copolymer Immobilized on Cotton Fabrics by Cross-Linker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27372–27381. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c03290.
- Ueki, T.; Watanabe, M. Polymers in Ionic Liquids: Dawn of Neoteric Solvents and Innovative Materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 85, 33–50. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20110225.
- Das, A.; Babu, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Van Guyse, J.F.R.; Hoogenboom, R.; Maji, S. Poly(-isopropylacrylamide) and Its Copolymers: A Review on Recent Advances in the Areas of Sensing and Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402432. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202402432.
- Jiang, L.; Qin, D.N.; Zhang, C.F.; Cui, J.B.; Xu, X.Y.; Hu, R.; Zhang, P.; Hu, L. Poly(-isopropylacrylamide) Microgel-Based Sensor for Clinical-Level X-ray Dose Measurements. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 10073–10080. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.3c01924.
- Bergbreiter, D.E.; Case, B.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Caraway, J.W. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) soluble polymer supports in catalysis and synthesis. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 6053–6062. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma980836a.
- Liu, M.; Song, X.; Wen, Y.T.; Zhu, J.L.; Li, J. Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate—Poly(-isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35673–35682. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b12849.
- Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.G.; Byun, J.Y.; Jang, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Spinks, G.M.; Kim, S.J. Biomimetic Thermal-sensitive Multi-transform Actuator. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7905. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44394-x.
- Maeda, S.; Hara, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yoshida, R.; Hashimoto, S. Self-walking gel. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3480–3484. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200700625.
- Shibayama, M. Physics of polymer gels: Toyoichi Tanaka and after. Soft Matter. 2025, 21, 1995–2009. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sm01418a.
- Takeoka, Y.; Watanabe, M. Polymer gels that memorize structures of mesoscopically sized templates. Dynamic and optical nature of periodic ordered mesoporous chemical gels. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5977–5980. https://doi.org/10.1021/la020133t.
- Yoshida, R.; Uchida, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Sakai, K.; Kikuchi, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Comb-Type Grafted Hydrogels with Rapid De-Swelling Response to Temperature-Changes. Nature 1995, 374, 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/374240a0.
- Yasumoto, A.; Gotoh, H.; Gotoh, Y.; Bin Imran, A.; Hara, M.; Seki, T.; Sakai, Y.; Ito, K.; Takeoka, Y. Highly Responsive Hydrogel Prepared Using Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Grafted Polyrotaxane as a Building Block Designed by Reversible Deactivation Radical Polymerization and Click Chemistry. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 364–374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.6b01955.
- Jochi, Y.; Seki, T.; Soejima, T.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M.; Takeoka, Y. Spontaneous synthesis of a homogeneous thermoresponsive polymer network composed of polymers with a narrow molecular weight distribution. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 840–848. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-018-0074-x.
- Okaya, Y.; Jochi, Y.; Seki, T.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M.; Hoshino, T.; Nakatani, T.; Fujinami, S.; Takata, M.; Takeoka, Y. Precise Synthesis of a Homogeneous Thermoresponsive Polymer Network Composed of Four-Branched Star Polymers with a Narrow Molecular Weight Distribution. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 374–386. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.9b01616.
- Kwon, D.; Jochi, Y.; Okaya, Y.; Seki, T.; Satoh, K.; Kamigaito, M.; Hoshino, T.; Urayama, K.; Takeoka, Y. Nonturbid Fast Temperature-Responsive Hydrogels with Homogeneous Three-Dimensional Networks by Two Types of Star Polymer Synthesis Methods. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 5750–5764. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.1c00446.
- Hiei, Y.; Ohshima, I.; Hara, M.; Seki, T.; Hoshino, T.; Takeoka, Y. Shrinking rates of polymer gels composed of star-shaped polymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and dimethylacrylamide copolymers: the effect of dimethylacrylamide on the crosslinking network. Soft Matter. 2022, 18, 5204–5217. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sm00402j.
- Gao, G.H.; Hara, M.; Seki, T.; Takeoka, Y. Synthesis of thermo-responsive polymer gels composed of star-shaped block copolymers by copper-catalyzed living radical polymerization and click reaction. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2024, 25, 2302795. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2024.2302795.
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H. Polymer Physics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. doi: 10.1093/oso/9780198520597.001.0001
- Li, X.; Nakagawa, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Shibayama, M. Polymer gel with a flexible and highly ordered three-dimensional network synthesized via bond percolation. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax8647. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax8647.
- Shibayama, M. Spatial inhomogeneity and dynamic fluctuations of polymer gels. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1998, 199, 1–30. doi: 10.1002/macp.1998.021990101
- Matsunaga, T.; Sakai, T.; Akagi, Y.; Chung, U.; Shibayama, M. Structure Characterization of Tetra-PEG Gel by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1344–1351. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma802280n.
- Tanaka, T.; Ishiwata, S.; Ishimoto, C. Critical Behavior of Density Fluctuations in Gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 38, 771–774. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.38.771.